The second most valuable crypto, Ethereum, has revamped its platform to reduce its carbon footprint on Earth, and the process was called The Merge.
Ethereum 2.0 is an upgraded version of Ethereum intended to make it significantly faster, less expensive, and more scalable. After The Merge, Ethereum 2's structure and design have some fundamental changes compared to its classic version. The two major changes are “Proof-of-Stake” and “Sharding”, which we would talk about further in the blog.
The classic Ethereum network can handle about 25 to 30 transactions per second, however, Ethereum 2.0 has the capability to handle 10,000 transactions per second, which is way faster. Implementing the Sharding technique would allow for increasing the level of scalability, recording transactions 64 times faster than the classic Ethereum network.
Difference between Ethereum 1.0 and Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum 1.0 | Ethereum 2.0 |
| Works on proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism, which is energy intensive | Works on proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, which is energy efficient |
| Can handle about 25-30 transactions per second | Can handle about 10,000 transactions per second |
| Transactions are verified by the multiple miners | Transactions are verified by the validators who staked Ethereum in the blockchain |
| The monetary policy is fixed | The monetary policy is variable |
| Database is replicated | Database is fragmented |
| Ethereum class has high security | Ethereum class has high performance |
Validators of Ethereum 2.0
Validators, the most important aspect of Ethereum 2, are responsible for its infrastructure and maintenance. Every validator has a Signing Key and a Withdrawal Key.
1. Signing Key:
It performs actions on the blockchain, like proposing and adding blocks to the Beacon Chain or one of the shard chains, attesting to the validity of the beacon and shard chain, and reporting malicious behavior by other validators.
2. Withdrawal key:
It performs actions on the funds to withdraw or transact ETH funds. The withdrawal key doesn't need to be available all the time. However, it needs to be safely secured, as the person with the withdrawal key has control over all the funds.
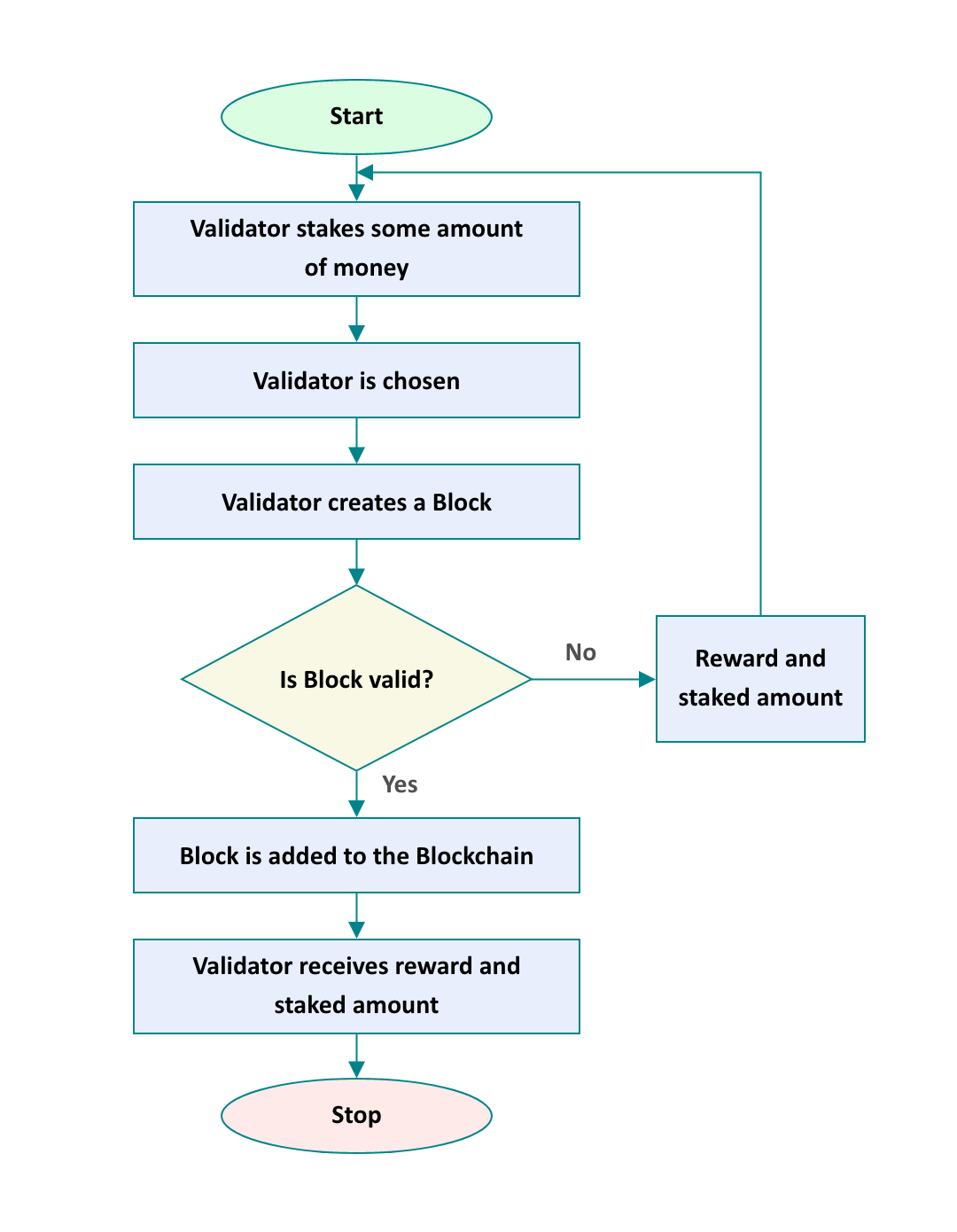
If you want to become a validator, you need to lock up 32 ETH in the beacon chain as collateral in case of any fraud or dishonesty. Validators do not work alone. They mostly work in committees, wherein groups of validators (minimum 128) vote on the head of the blockchain.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
After The Merge, the Ethereum mainnet has been switched from an energy-intensive proof-of-work to an energy-efficient Proof-of-stake consensus mechanism. The major role of PoS is to propose new blocks and provide computing power, storage, and bandwidth to validate the transactions. There are validators instead of miners. These validators are given periodic payouts in ETH.
Ethereum 2 uses proof-of-stake, where validators stake a capital of 32 ETH into a smart contract on Ethereum. This staked ETH then acts as collateral that can be destroyed if the validator behaves dishonestly or lazily. The validator can be slashed from (forced to leave) the beacon chain if it receives a certain number of penalties. It is the validator's responsibility to validate the new blocks propagated over the network. They can occasionally create and propagate new blocks themselves.
Proof-of-stake is faster and more eco-friendly than proof-of-work, because of its less power consumption. PoS increases the network’s scalability and reduces its energy usage by approximately 99.95%.
Proof-of-stake comes with a number of improvements over the proof-of-work consensus mechanism:
- Better energy efficiency – PoS consumes far less energy (99.95% less) than PoW for validating the same transactions
- Lower entry barriers and reduced hardware requirements – No need for hefty and elite hardware to become a validator and create new blocks
- Reduced centralization risk – PoS leads to more nodes, resulting in a more secure network
- More participation is appreciated with fewer ETH issuance to incentivize them
- Costlier for frauds and misbehaves by economic penalties of 51% style attacks exponentially, compared to PoW
- In case of a 51% attack on the crypto chain, the community has a provision for the social recovery of an honest chain.
Sharding in Ethereum 2.0
Sharding is the process of splitting one blockchain into multiple blockchains called shards, making the entire network more efficient. Every validator maintains information related to their shard. The validators are also shuffled between shards on a regular basis to avoid any kind of manipulation. Communication and coordination of the shards are done using the Beacon Chain. As mentioned, Sharding helps in achieving the level of scalability. 64 “Shard Chains” are put to use, which runs through transactions in parallel. Hence, recording transactions is 64 times faster than the classic Ethereum network.
Advantages of Ethereum 2.0
- Increased Scalability: After the Merge, Ethereum supports thousands of transactions per second in a cost-efficient manner. Sharding and PoS have added more nodes in the chain, reducing the power consumption to very minimal.
- Greater Security: Thanks to the Beacon Chain, designed to help with network security, Ethereum 2 is developed as secure as possible to thwart attacks. This security makes users and institutions feel comfortable using the platform.
- Greater Sustainability: Reduced carbon footprints result in greater sustainability. In order to sustain the blockchain as a service, power consumption must be maintained and minimized as much as possible. The PoW consensus algorithm used to consume a great deal of energy, which is not the case with Ethereum 2.0's PoS as there is no more mining involved. According to Ethereum Co-Founder Vitalik Buterin, Ethereum’s energy consumption will be diminished “by a factor of more than 1,000” with PoS.
How is Ethereum 2.0 more secure?
With the most important advantage of Ethereum 2.0 is its scalability. Ethereum 2.0 has shard chains, due to which it can conduct up to 10,000 transactions per second, whereas the classic Ethereum can support only 30 transactions per second. So a lot of delays and network congestion are avoided with Ethereum 2.0.
Ethereum 2.0 requires a large set of validators, approximately 16,384, which makes it more decentralized, secure, and less prone to manipulation.
Endnote
To conclude, blockchain has evolved quite a lot from its early stage. Ethereum 2.0 paved the way for energy-efficient crypto with increased security. Yet, there is a lot to achieve and with every baby step, blockchain is evolving.
We, at Seaflux, are Blockchain enthusiasts who are helping enterprises worldwide. Have a query or want to discuss Blockchain projects? Schedule a meeting with us here, we'll be happy to talk to you.

Jay Mehta
Director of Engineering